5G is another big speed increase and function supplement after 4G data transmission and information communication. Nowadays, many industrial applications expect 5G to bring breakthrough solutions to many current application scenarios involving data transmission and information communication.
Due to the emergence and continuous advancement of the NSA (Non-Independent Networking) standard in 2017, the world's major operators have also intensified their layout and adjustment for their respective future plans. For the 5G roadmap released by the earlier 3GPP, 5G commercial is likely to Again in advance. This also brings back thinking about application scenarios, frequency band allocation and operator layout strategies.
At the 7th EEVIA China ICT Media Forum and 2018 Industry and Technology Outlook Seminar, Mr. Tao Zhen, Senior Manager of Market Strategy of Qorvo Asia Pacific Mobile Division, analyzed and shared related issues.

5G three application scenarios
As shown in Figure 1, the three major application scenarios of the future 5G recognized by the ITU and 3GPP include enhanced mobile broadband, IoT in the 5G era, and high-reliability low-latency scenarios.
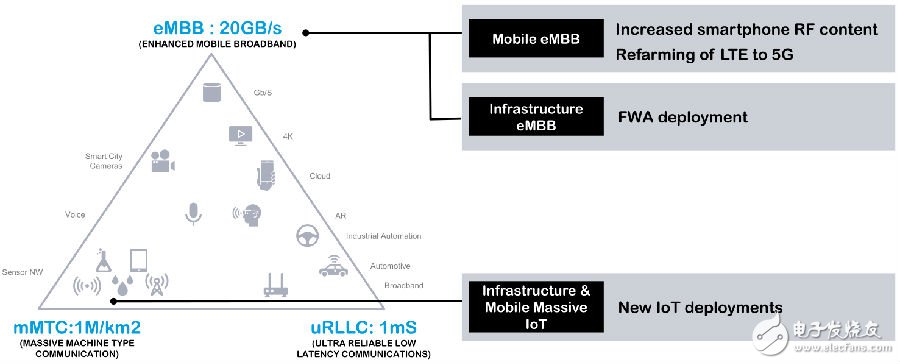
Figure 1 5G three application scenarios
Among them, the IoT of the 5G era must distinguish between the 4G era. The NB-IoT, eMTC, and Cat-M1 we are talking about now are based on the IoT of the 4G LTE era. Such mMTC can also be understood as the IoT based on the 5G standard. High-reliability and low-latency application scenarios include today's autopilot, AR/VR, and many other applications that require high reliability and real-time performance.
Mobile phone application 5G challenges
Enhanced mobile broadband is still the main application scenario of 5G, and it also faces many challenges. Now, taking mobile phones as an example for analysis, there are three major challenges:
1) Since it is to support 5G and is backward compatible with 3G and 4G, it will add more new RF semiconductor devices that are different from traditional 4G, including filters, switches, power amplifiers, and integrated front-end modules. Demand from the new 5G frequency band, standards and commissioning methods.
2) The definition of the frequency band is another problem. In addition to the newly defined 5G frequency band, there will be some 4G spectrum in 2020, and even later to 5G, which requires new RF devices to support the 5G-NR standard on the basis of existing 4G RF semiconductors.
3) There will also be new challenges in infrastructure. For example, the commercial use of millimeter waves on 5G, millimeter wave. At present, it may take 3-5 years for commercial use in China. In the United States, where the application is relatively high, this year, the millimeter wave has been commercialized at 5G. Called FWA (Fixed Wireless Access). FWA is not a traditional mobile terminal application scenario. Therefore, the US 5G-based 5G is not applied to mobile devices or scenarios, and it also brings the infrastructure requirements that distinguish traditional mobile devices.
The last mile of domestic broadband is the fiber-optic mode, which requires the fiber to be connected to the building, and the cable must be buried underground. Now, in the United States, using millimeter-wave FWA (Fixed Wireless Access) to solve the last mile problem no longer needs to be wired, but in this way, your access device at home is just a fixed access device. Not a mobile device, and not a battery-powered device, it is a device that requires power. And this is another application scenario that is different from the real 5G mobile smartphone.
4) In terms of system architecture, more consideration needs to be given to how the front-end architecture is implemented, including how many antennas you need and how to do the antenna division. In the future 5G mobile phone communication, in addition to the impact of pure radio frequency semiconductors, more need to consider the system architecture, taking the antenna division of labor as an example, to achieve better antenna division requires antenna division, multiplexer, etc., in the future In the 5G front-end architecture, in addition to traditional RF transceivers such as PAs, filters, and LNAs, you need to consider more about how the front-end antennas are allocated, and how the multiplexers can better support carrier aggregation. Since the antenna division has different combinations (different frequency bands and different functional combinations), in the future 5G smart phones, the antenna division is a relatively large device, which is also a new one derived from 5G. Device front-end device. In addition, because you have more and more antennas, but you also want a wider coverage of an antenna on your mobile phone, the antenna tuning technology will be used more in the 4G era than in the 4G era.
5G commercial time ahead
Figure 2 shows the roadmap time division of 3GPP for the entire 5G application. As can be seen from the figure, since 2018, all national operators have started trial commercialization, but the real large-scale commercial use will still be in the second half of 2020, or even until 2021.
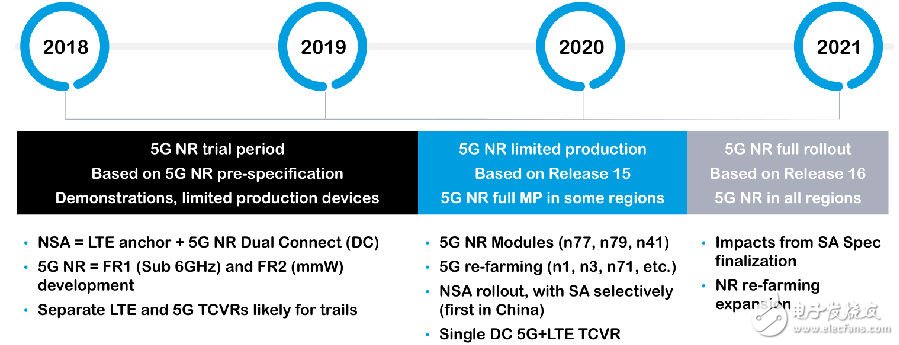
Figure 2 3GPP roadmap time division for the entire 5G application
Mr. Tao Zhen, Senior Manager of Market Strategy, Qorvo Asia Pacific Mobile Division, said that from now until the first half of 2019, more operators will do 5G trial commercialization, mainly because there is no real standard before. With the development of the first edition of the NSA (Non-Independent Networking) standard in December 2017, the first version of the SA (Independent Networking) standard will be completed in June 2018, which will accelerate the commercialization of 5G networks. From the second half of 2019 to 2020, there will be more 5G commercials based on the 15th version of 3GPP, which may have large-scale commercial use in some countries, including the goal of three operators in China, all of which are expected to be under 2019. In the first half of the year and early 2020, 5G commercialization will be officially realized. However, during this period, operators will definitely have different types of planning. At present, only China Mobile and China Telecom will take independent network routes. All other operators' current plans are non-independent networking. From 2020 to 2021, it will be a real 5G large-scale commercial. All independent networks supporting 5G and non-independent networking will be commercialized by 2020.
In addition, the use of non-independent networking forms also has a certain impact on the RF front-end. Since the non-independent networking relies on LTE as the core network, all voice communication layers and control layers are LTE, and the data layer is 5G data. This means that the RF front-end must have an LTE channel. No matter which frequency band, there must be A 5G channel works at the same time, which will inevitably cause mutual interference problems.
According to Mr. Tao Zhen, in the current stage, mainstream chips companies including Qualcomm, Intel, and HiSilicon may make 5G-NR new transceiver chips and 4G LTE chips into two chips in mobile chips. After 2019, we see more generations based on 5G-NR modules.
Global operator layout
The choice between SA and NSA
From the current planning point of view, the vast majority of operators are taking NSA, and only China Mobile and China Telecom are taking SA. And why are there different options? Especially why the two domestic operators will love SA alone, this issue is also necessary to analyze it here.
From a cost perspective, NSA has a big advantage. To make an SA network, all the re-investment needs to be made, including your core network, access network, and data link network are all based on 5G-NR, and the investment is quite large; while the NSA can be based on the core network of 4G-LTE. To access the network, you only need to do 5G base station deployment in the data layer.
In terms of function, SA pulled back more than one point. Many people think that 5G is faster than 4G, but from the operator's point of view, in addition, 5G has many functions that cannot be realized in the 4G era, such as network virtualization management and network slicing. So in this respect, the networking of the NSA is not a complete 5G network. The NSA is only a transition to the middle of 5G commercialization. In the future, most commercial 5G networks will transition to SA, which is why China Mobile and China. The first step in telecommunications is to choose the reason for doing SA.
Spectrum planning
At present, the 5G deployment is in the forefront of China, the United States, Japan and South Korea. Among them, China currently has two frequency bands within 6GHz, including 300MHz bandwidth from 3.3GHz to 3.6GHz, and 200MHz bandwidth from 4.8GHz to 5GHz. The specific allocation of the three major operators has yet to be released.
In foreign countries, Japan and South Korea will commercialize the spectrum of the centimeter band in 2020, specifically in the 3.5 GHz and 4.8 GHz bands. In the United States, because there is no frequency band of centimeter wave available in the field of mobile communications, its spectrum is from 3.5G to 3.7G 150 megabytes, and no longer used in mobile communications, so its focus is on millimeter wave applications. Of course, US regulators are discussing the need to open more C-band spectrum to 5G in the future, but there is still no accurate point in time.
Qorvo's 5G commercial development plan
Qorvo has developed the first RF front-end module based on the new 5G NR standard since 2017. Currently, it supports the 5G smart phone. Mr. Tao Zhen said that whether it is independent network or non-independent networking, whether it is from technology The angle of support or the angle of support is ready. In February 2018, China Mobile released the “5G Terminal Pioneer Programâ€. Based on the “5G Terminal Pioneer Programâ€, China Mobile and 20 global terminal industry partners are expected to launch the first batch of 5G in line with China Mobile demand by the end of 2018. Chips, the first batch of 5G pre-commercial terminals released in the first half of 2019, including data terminals, smart phones and other products, Qorvo was also invited to join the program. Qorvo's goal is to officially mass-produce 5G RF semiconductor products of 3.5G and 4.8G in the first half of 2019. In line with the major domestic mobile phone manufacturers, especially Chinese operators, 5G will be realized in the second half of 2019 to the first half of 2020. Formal commercial use.
Made of TPU material imported from South Korea, it can effectively protect the screen from unnecessary wear or scratches and reduce the impact of falling.
The flexible material design allows the Screen Protector to adapt to the contours of any device, so it can be connected to curved displays and rounded edges. The Full-Cover Screen Protector can perfectly fit your screen and provide maximum protection.
The oleophobic coating technology protects the glass from fingerprints left by sweat and grease, and fully supports the 3D touch function on the iPad.
The ultra-transparent thickness of 0.14mm ensures the sensitivity of the original touch screen. When using Apple Pencil, it can still maintain a high touch sensitivity. 99% transparency provides an ideal natural viewing experience.
If you want to know more about Imported Screen Protector For iPad products, please click the product details to view the parameters, models, pictures, prices and other information about Imported Screen Protector For iPad.
Whether you are a group or an individual, we will try our best to provide you with accurate and comprehensive information about the Imported Screen Protector For iPad!
Screen Protector For iPad, Imported Screen Protector, 200*300 Screen Protector, Imported Protective Film, iPad Screen Protector,Imported Hydrogel Film
Shenzhen Jianjiantong Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.jjtbackskin.com