Carrier aggregation (Carrier AggregaTIon) technology will help accelerate the popularization of Long Range Evolution (LTE). The use of LTE frequency bands is too chaotic, which has become a major challenge for global telecom operators to build infrastructure. Therefore, chip and equipment vendors have actively introduced carrier aggregation technology to help telecom operators improve frequency band utilization and flexibility of use to speed up their business transformation .
As consumers increasingly demand mobile network bandwidth, how to effectively handle data traffic has become an important selling point for smartphones, tablet devices, and other data computing equipment. To this end, the working organization responsible for promoting the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM), Broadband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA), and Long-Term Evolution Project (LTE)-3GPP, began investing in the next phase of mobile research as early as several years The direction of communication technology evolution to meet the future mobile market demand for data-centric wireless solutions.
Improve spectrum efficiency / bandwidth LTE carrier aggregation
4G LTE helps unify mobile communication technologies and improves the chaotic situation of diversified development of various technologies in the past 2G and 3G eras. 4G equipment will also bring new profit opportunities for telecom, chip and terminal brands. However, due to the complexity of the frequency bands available worldwide, how to solve the problem of frequency band support will be the biggest challenge for the above mentioned companies.
Taking GSM as an example, four frequency bands must be supported to cover the global range, and five frequency bands are required for WCDMA and high-speed packet access (HSPA). As of December 2012, more than ten frequency bands have deployed LTE, and the number is still Will continue to increase.
This decentralized frequency band is the result of the spectrum allocation determined by each region. Of course, countries also plan to designate some frequency bands as global roaming bands to solve the problem of too many frequency bands, but there is still no clear progress. By 2014, a device may have to support five to six frequency bands to meet the requirements of a telecommunications operator; moreover, in the future, LTE will be expected to use up to about 18 frequency bands worldwide (Figure 1), which means high Efficient multi-band support is essential to solve the global problem of equipment.
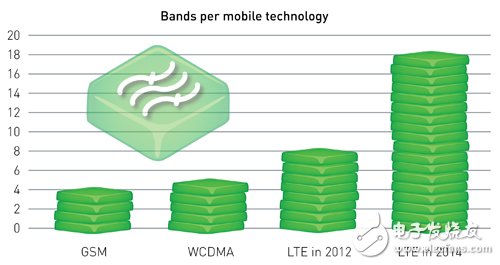
Figure 1: Trends in the number of frequency bands supported by mobile communications technology
In fact, long before the LTE standard was released, many telecom operators began to prepare for the next deployment of LTE-Advanced. This technology proposes the concept of carrier aggregation (Carrier AggregaTIon, CA), which will bring higher network to end users. Road efficiency and transmission rate, and support various advanced application scenarios.
Since bandwidth and data throughput are two typical positive correlation factors, the larger the bandwidth, the higher the throughput. Generally speaking, a mobile phone uses only one carrier in one frequency band at a time. By integrating two frequency bands or multiple carriers in the same frequency band (Figure 2), so-called carrier aggregation can be achieved and more radio frequencies can be used ( RF) resources to expand the effective bandwidth. At present, in all continuous spectrum allocation, more than 90% of the spectrum can only be vacated with a bandwidth of 15MHz or lower, and most of it is even lower than 10MHz. This restriction requires many operators to use carrier aggregation, otherwise it is difficult to support 100Mbit / s or higher transfer rate.
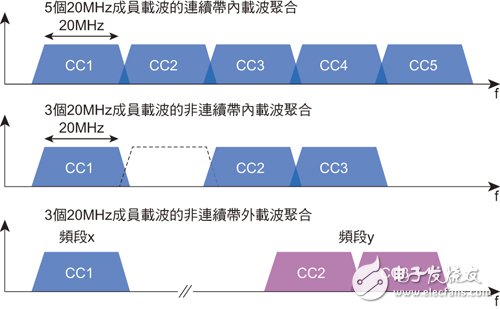
Figure 2: Conceptual diagram of carrier technology
In particular, the U.S. spectrum resource is very finely cut, and the fragmentation situation is serious. Few operators have continuous 20MHz spectrum. Therefore, the U.S. market will be one of the main driving forces of carrier aggregation technology in the future. It will be launched in 2013 and is expected to further expand its scale of development in 2014.
In addition, South Korean and Japanese telecommunications companies also have substantial carrier aggregation solutions. The first phase will aggregate up to 20MHz of spectrum to allow users to obtain 150Mbit / s of downstream data transmission rate. This number will be even higher in the future. At the same time, European telecom operators also intend to use carrier aggregation, but are not in a hurry to promote it, because operators already have 20MHz spectrum resources in the 1.8 or 2.6GHz band.
The name of wireless router can be separated out of two keywords: wireless and routing. Understand the technical principle behind these two words, you understand the wireless router.
Wireless is also what we often call Wi-Fi. Wireless routers can convert home broadband from wired to wireless signals, and all devices can happily surf the Internet as long as they connect to their own Wi-Fi. In addition, these devices also form a wireless local area network, where local data is exchanged at high speed and is not limited by the bandwidth of home broadband.
For example, many people have smart speakers in their homes that can be used to control various smart appliances. When you say small X small X, turn on the TV, the speaker actually finds the TV through the LAN and sends instructions, and does not need to connect to the Internet; And if you let it broadcast news, you have to get data through the Internet.
The Local Area Network we talked about earlier, also known as the Intranet, is represented by the Local Area Network (LAN) on the router, so the Wi-Fi signal is also called WLAN(Wireless LAN); The Internet we want to access, also known as the extranet, is represented on the router by the WAN(Wide Area Network).
On the Intranet, the IP address of each device is different, which is called a private address. All devices on the Internet share the same public address, which is assigned by broadband operators such as China Telecom Unicom.
The router is the bridge between the Intranet and the external network. The above mentioned IP address translation, packet forwarding, is the router routing function.
In other words, the router is the hub of the home network, and the data of all the devices must be forwarded through it to access each other or reach the external network, which means that one husband is the key and ten thousand men are not open, so the comprehensive router is also called "home gateway".
Wireless Router,Wifi 6 Wireless Router,Mesh Wifi Router,Wifi Routers For Home
Shenzhen MovingComm Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.movingcommtech.com