Transformer use is to transform AC voltage, current and impedance devices.
The principle of the transformer is that when there is an alternating current in the primary coil, an alternating magnetic flux is generated in the core (or core), so that a voltage (or current) is induced in the secondary coil.
The structure of a transformer consists of a core (or core) and a coil. The coil has two or more windings, wherein the winding of the power supply is called the primary coil and the rest of the winding is the secondary coil.
First, the principle of transformer production:
In a generator, whether the coil moves through a fixed coil through a magnetic field or a magnetic field, a potential can be induced in the coil. In both cases, the value of the magnetic flux does not change, but the amount of magnetic flux that intersects the coil has Change, this is the principle of mutual induction. A transformer is a device that uses electromagnetic induction to convert voltage, current, and impedance.
Second, the classification of transformers
Classified by cooling method: dry (self-cooling) transformers, oil-immersed (self-cooling) transformers, and fluoride (evaporative cooling) transformers.
According to moisture classification: open transformers, potted transformers, sealed transformers.
According to core or coil structure classification: core type transformer (insert core, C type core, ferrite core), shell type transformer (insert core, C type core, ferrite core), Toroidal transformers, metal foil transformers.
According to the number of phases of the power supply: single-phase transformers, three-phase transformers, multi-phase transformers.
Classified by purpose: power transformers, regulator transformers, audio transformers, intermediate frequency transformers, high frequency transformers, pulse transformers.
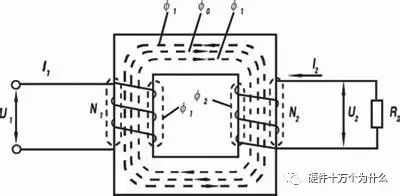
Third, the characteristics of power transformer parameters
working frequency:
Transformer core loss is related to the frequency, so it should be designed and used according to the frequency of use. This frequency is called the operating frequency.
rated power:
At a specified frequency and voltage, the transformer can operate for long periods of time without exceeding the output power of the specified temperature rise.
Rated voltage:
Refers to the voltage allowed to be applied to the coil of the transformer and must not exceed the specified value during operation.
Voltage ratio:
Refers to the transformer primary voltage and secondary voltage ratio, there is no load voltage ratio and load voltage ratio difference.
No-load current:
When the transformer secondary is open, the primary still has a certain current. This part of the current is called the no-load current. The no-load current consists of a magnetizing current (flux producing) and an iron loss current (caused by the core loss). For a 50Hz power transformer, the no-load current is substantially equal to the magnetizing current.
Load loss:
Refers to the power loss measured at the primary when the transformer secondary is open. The main loss is the core loss, followed by the loss (copper loss) of the no-load current on the copper resistance of the primary coil. This part of the loss is very small.
effectiveness:
Refers to the percentage of the ratio of secondary power P2 to primary power P1. In general, the higher the rated power of the transformer, the higher the efficiency.
Insulation resistance:
Indicates the insulation performance between the transformer coils and between the coils and the iron core. The level of insulation resistance is related to the performance of the insulating material used, the temperature and the degree of humidity.
IV. Characteristics of audio transformers and high frequency transformers
Frequency response:
Refers to the transformer secondary output voltage characteristics with the operating frequency changes.
Passband:
If the output voltage of the transformer at the intermediate frequency is U0, the frequency range when the output voltage (input voltage remains unchanged) falls to 0.707U0, which is called the passband B of the transformer.
Initial and secondary impedance ratio
The initial and secondary impedances of the transformer are connected to the appropriate impedances Ro and Ri to match the primary and secondary impedances of the transformer. The ratio of Ro and Ri is called the primary and secondary impedance ratio. In the case of impedance matching, the transformer works in the best condition and has the highest transmission efficiency.
Fifth, the technical parameters of low frequency transformer
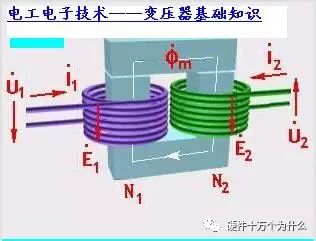
Transformer principle structure diagram
Different types of transformers have corresponding technical requirements and can be represented by corresponding technical parameters. For example, the main technical parameters of the power transformer are: rated power, rated voltage and voltage ratio, rated frequency, operating temperature level, temperature rise, voltage regulation rate, insulation performance and moisture resistance. The main technical parameters for general low-frequency transformers are: transformer ratio, frequency characteristics, nonlinear distortion, magnetic shielding and electrostatic shielding, and efficiency.
Voltage ratio:
The number of coil turns of the two sets of transformers is N1 and N2 respectively, N1 is primary, and N2 is secondary. Adding an AC voltage to the primary coil generates induced electromotive force across the secondary coil. When N2>N1, the induced electromotive force is higher than the voltage applied by the primary. This type of transformer is called a step-up transformer: when N2
In the formula, n is called voltage ratio (turn ratio). When n <1, then N1> N2, V1> V2, the transformer is a step-down transformer. The reverse is a step-up transformer.
Transformer efficiency:
At rated power, the ratio of the output power of the transformer to the input power is called the efficiency of the transformer.
Where η is the efficiency of the transformer; P1 is the input power and P2 is the output power.
When the transformer's output power P2 is equal to the input power P1, the efficiency η is equal to 100% and the transformer will not generate any losses. But in fact this type of transformer is not available. Transformers always produce losses when they transmit electrical energy. Such losses include copper losses and iron losses. Copper loss is the loss caused by the transformer coil resistance. When the current heats up through the coil resistance, some of the electrical energy is converted into heat energy and lost. As the coils are generally wound with insulated copper wires, they are called copper losses.
Transformer iron loss includes two aspects. The first is the hysteresis loss. When the alternating current passes through the transformer, the direction and magnitude of the magnetic flux through the transformer silicon steel sheet will change, causing the internal molecules of the silicon steel sheet to rub against each other and release heat energy, thereby depleting part of the electrical energy. This is the hysteresis loss. . The other is eddy current loss when the transformer is working. There are magnetic lines passing through the iron core, and an induced current will be generated in the plane perpendicular to the magnetic force lines. Since this electric current forms a closed loop and becomes a vortex, it is called a vortex. The presence of eddy currents causes the core to generate heat and consume energy. This loss is called eddy current loss.
The efficiency of the transformer is closely related to the power level of the transformer. Generally, the greater the power, the smaller the loss-to-output power ratio and the higher the efficiency. Conversely, the smaller the power, the lower the efficiency.
10 inch tablet is the most important size on tablet market. Which kind of clients like more? The answer is loving bigger size or storage, longer working time, etc. Since Android Tablet 10 inch is usually equipped with full HD screen, memory support up to 8GB, storage up to 256GB, battery up to 7000mAh-working 5-8hours. However, 8 inch android tablet mainly up to 4GB ram 64GB ROM, 4000mAh battery. At this store, you can see more than ten different 10 inch tablets on sale and one 10 inch windows tablet with magnetic keyboard option, and high level CPU and SIM Card option. Besides, you can also see amazon tablet 10 inch with competitive cost, especially take above 1000pcs. Except android tablet, 14 inch 64Gb Student Laptop for online learning, 15.6 inch celeron n5095 business laptop, 15 inch intel i3, i5, i7 10th or 11th generation Gaming Laptop and 16 inch laptop with 4gb graphics card and 16gb ram 512GB ssd alternatives also.
Any other special requirements, just fee free to contact us. Will try our best to support you.
10 Inch Tablet,10 Inch Tablets On Sale,Android Tablet 10 Inch,Amazon Tablet 10 Inch,10 Inch Windows Tablet
Henan Shuyi Electronics Co., Ltd. , https://www.shuyiaiopc.com