Now I am talking about the "second half" of the Internet. What is the second half of the game? Different people have different opinions? If the early Internet born in the PC era is the first stage of Internet development, and the mobile Internet after the development of smart phones is the second stage of the Internet, then the Internet is about to usher in a new era, the Internet of Things era.

The next stage of the mobile Internet: the Internet of Things era
The concept of Internet of Things (IoT: Internet of Things) is no longer a new concept. As early as Premier Wen’s "perceive China" in 2009, the government work report has officially listed the Internet of Things as one of the country's five emerging strategic industries. In the years since then, the media has been popularizing and promoting the concept of the Internet of Things to the public.
What is the Internet of Things, not just RFID, but also networking
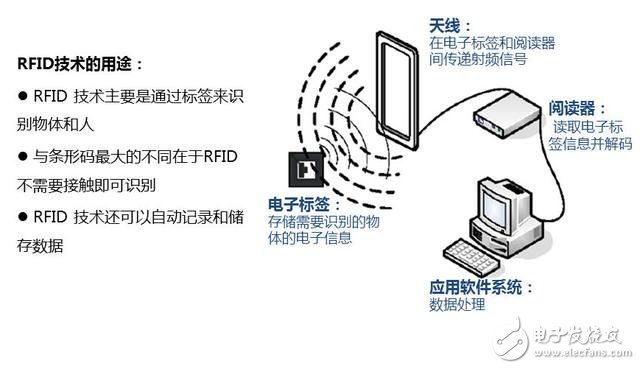
RFID technology has been widely used in manufacturing, logistics and retail
In 1999, Professor Kevin Ash-ton of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) first proposed the concept of the Internet of Things, namely through radio frequency identification (RFID), infrared sensors, global positioning systems, laser scanners, gas sensors and other information sensing. Equipment, a network that connects any item to the Internet in accordance with a contracted agreement for information exchange and communication to enable intelligent identification, location, tracking, monitoring and management. In the early days, the Internet of Things was generally a logistics network based on radio frequency identification (RFID) technology.
Now when we talk about the Internet of Things, the first thing I think of IoT technology is RFID. RFID has become synonymous with the Internet of Things. Although the earliest Internet of Things and RFID technology are closely integrated, the concept of the Internet of Things has already surpassed RFID.
On November 17, 2005, at the World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS) in Tunis, the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) issued the "ITU Internet Report 2005: Internet of Things", citing the concept of "Internet of Things." The definition and scope of the Internet of Things has changed, and the coverage has been greatly expanded. It is no longer just an Internet of Things based on RFID technology.
RFID technology solves the identification of objects, mainly used in logistics networks, to facilitate the identification and tracking of objects by information systems. But the Internet of Things is not only about identifying objects, but also about having networking capabilities and realizing the interconnection of everything.
At present, IoT devices mainly use short-range communication technologies with transmission distances of less than 100m, such as Wifi, Bluetooth, etc.
So how do current smart hardware or IoT devices actually connect to the Internet? There are many networking technologies available today, mainly short-range wireless communication technologies, including Bluetooth, Wifi, Zigbee, ANT+, and so on. Zigbee is generally used in the industrial field, ANT+ is used in the sports field, and Bluetooth and Wifi are the most used communication methods for home IoT devices or smart hardware.
A smart home system based on the Zigbee protocol requires a gateway device for protocol conversion to be interconnected with the user terminal.
Many smart wearable devices use Bluetooth to synchronize data with mobile phones, and then upload data to the cloud through mobile phones; Wifi-based devices use Wifi routers to synchronize data to the cloud; devices based on other networking technologies, such as Zigbee, generally need to perform The protocol-switched gateway connects to the user's phone or computer or synchronizes data to the cloud.
What are the problems that restrict the widespread use of smart wearable devices?
Current smart wearable products need to rely on smartphones to sync data to the cloud.
Smart wearable devices are widely used. Currently, there are two technical limitations, one is coverage and the other is power consumption. The former restricts the networking capability of smart wearable devices, and the latter restricts the endurance capability.
Single core armored cable
Standard: IEC 60502
Rated Voltage: 0.6/1kV
AWA (Aluminium Wire Armour)
SSWA ( Stainless Steel Wire Armour)
Sheath/Jacket: PVC (Polyvinyl-Chloride)
Applications: Armoured Cable for power networks, industrial plants, switch-boards, underground and in cable ducting where better mechanical protection is required.
Single Core Armored Cable,Types Of Armoured Cable,Single Core Wire,Armored Cable Power
Shenzhen Bendakang Cables Holding Co., Ltd , https://www.bdkcables.com