LCDs and OLEDs are two completely different display technologies that are currently widely used in smartphones and flat panel TVs. In addition, there are old technologies like plasma that have existed in the TV field, but they have disappeared. At present, most users can only choose between these two display panel products, and if you don't know how to choose, this article will tell you some basic knowledge and tell you the difference between LCD and OLED, and tell you How to strike a balance between demand and budget.
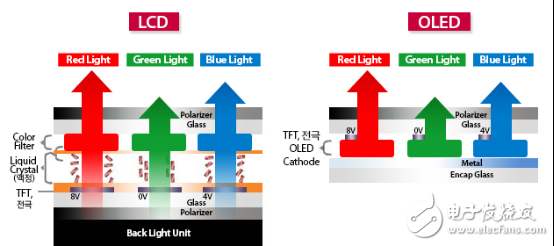
LCD display
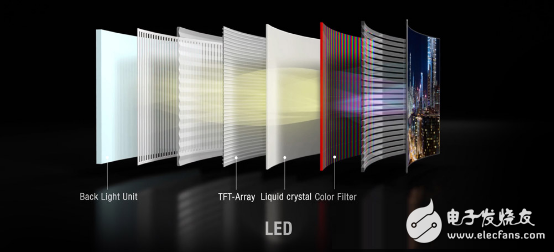
The entire LCD is called LiquidCrystalDisplay, which creates a variety of colors based on white light passing through the color filter. The white light forms a basic color such as red, green, and blue after passing, and controls the color of each pixel by controlling the over-light ratio of each pixel.
In the LCD display, it is very difficult to completely shield the white light from displaying black. There will always be some light leakage, and this is why the real black cannot be displayed on most night display screens. s reason.
Passive and active matrix
LCD displays have been in use since the 1980s and have been used for the first time on "portable computers." These screens have a "matrix" array of pixels and are divided into active and passive matrices. The active matrix technology is more advanced and allows for finer control and faster switching speeds than passive matrices. Active matrix technology was first introduced using TFT-based matrix screens, but more variants have emerged, but they are basically the same working principle and the cost is decreasing.
LCD backlight
All LCD displays require some form of white backlighting, and backlighting technology continues to evolve over time. The purpose of the backlight is to have higher brightness, more uniform illumination, and make the display smaller, thinner, and lighter.
The LCD screen was originally used for CCFL backlighting, but has now been changed to LED backlighting. In addition, some LCD screens have not only used white backlights, but also combined with white LEDs of specific colors to achieve some more difficult purposes.
Although the backlights are all from the liquid crystal layer, most of the LED backlight sources come from the edge of the screen, usually at the border, and this design can make the screen thinner and flatter.
TV-like products are usually not as thick as the thickness requirements, so they use an overall uniform backlight, which can be more uniform and can be adjusted for local backlighting.
LCDIPS and PLS

The full name of IPS is In-PlaneSwitching (also known as SuperTFT), which is a variant of the LCD display. IPS provides better color accuracy and a broader perspective. Ordinary LCD displays usually display the best fresh fruit just in front of the screen.
IPS can completely replicate color effects in a range of 178 degrees without any impact. And that's why most touch devices now use IPS displays. Yes, the traditional LCD display will have strange effects when pressed with your fingers. I believe everyone has had a similar experience.
At the same time, IPS technology itself has more improved versions, including Super-IPS (S-IPS), Advanced SuperIPS (AS-IPS) and IPS-Pro, although not all IPS panels have the best results, but overall Said IPS is better than traditional LCD panels.
PLS (PlaneLineSwitching) is also a technology similar to IPS and is a patent of Samsung . Samsung said that this screen has better brightness and more efficient production costs, but it is still uncertain, because the absolute leader of IPS display on the market is LG.
LCD+ quantum dots

Quantum dots are a technique that increases the color and hue of LCD displays, and semiconductor nanobody quantum dots can absorb specific spectra, which usually depends on their size. This property can be used/created with better colors such as red, green and blue, which will give the user a more saturated color.
Quantum dot technology has recently been enthusiastically sought after by the market, and even has the strength and the latest technology OLEDs. However, quantum dot technology is currently only found in high-end LCD TVs, but it is believed to be popularized over time.
OLED screen

OLED stands for OrganicLightEmitTIngDiodes, and each pixel itself emits light without the need for a separate backlight or color filter. Each OLED pixel can be assigned red, green, and blue colors, and now manufacturers have added yellow, but the principles are the same.
Due to the special properties of the OLED, it is not necessary to cover the light source like the LCD when displaying black, but only the pixel is extinguished and not illuminated. And that's why OLED displays bring true "black." The black color of the OLED is very deep, the contrast is extremely high, and even an amazing effect can be produced if compared with elements such as white. OLED technology first appeared in the lab in 1987, and has become a very popular technology in the field of smart phones. Because the OLED screen is one layer less than the LCD screen, the thickness is controlled to be thinner, which is especially important for mobile devices. For TV products, whether to choose OLED products depends on the user's preferences. However, we believe that the ultra-thin OLED is not a decisive advantage for LCD TVs.
One-to-one comparison
Due to the differences in basic properties, we can look at the direct comparison between imaging techniques of two different principles, giving users a more intuitive experience.
Black level: OLED wins
The black level refers to the extent to which the picture can be "black" when displaying the darkest color. Since technologies such as LCD, DLP, or projection rely on filtering or shielding from white light, it is very difficult to display true black. In fact, it can be said that the LCD screen can't bring true black at all. After all, the shadowing effect is good, and there will still be some light leakage. On the other hand, due to the self-illumination principle, OLEDs can bring true black as long as the illumination mechanism is turned off.
Contrast: OLED wins
Contrast refers to the difference between the brightest white and the darkest black, while LCDs have an advantage in brightness (especially in HDR mode), while OLEDs have the deepest black. In general, OLED displays typically have higher contrast because the advantage at the black level will amplify this difference.
Perspective: OLED wins
Perhaps the best IPS screens are comparable to OLED displays, but most LCD screens are not as good as IPS (especially TVs and smartphones), so in addition to the top IPS display, In comparison with OLED, the LCD panel has a slightly worse viewing angle. In the face of OLED TV, regardless of the audience sitting at that angle, you can see the content on the screen with high quality feeling.
Color gamut: OLED wins
In terms of paper parameters, the advantages of OLED in the color gamut are not obvious, mainly because the LCD panel now introduces quantum dot technology. Basically, the best LGOLED TVs and Samsung's top-of-the-range quantum dot LCD TVs are comparable in color gamut performance.
However, usually only the best LCD TVs are comparable to OLED TVs, so overall color gamut performance is better.
Brightness level: LCD wins
Since LCD TVs typically use separate backlighting, they generally provide better brightness. In reality, the best LCD and OLED have a difference of about 400 NIT in brightness. In general, the LCD is superior in brightness level. Be aware that higher brightness will give the screen a better look in the outdoors or during the day. HDR
HDR mode can increase brightness by 1000 to 10000 NIT, while HDR-capable OLED TVs are comparable in brightness to LCD TVs. However, some Sony LCD TVs can increase the brightness to 1000 to 1300 NIT, so overall, LCD TVs are even brighter.
Color uniformity: OLED wins
Whether or not it is possible to display various colors on a single plane in a uniform manner is a very important indicator. Since the backlight of the LCD screen usually comes from the edge, it is relatively uniform in terms of uniformity of illumination. Discrete backlights provide better results if the backlight is evenly spread behind the screen.
On the other hand, OLEDs perform much better in this respect, since each pixel can emit light by itself, so there is no need for light source to spread. In real life, even OLED displays are not completely unified, and even flexible OLEDs appear, but overall it is still better than LCD.
Power consumption: LCD wins
At the same brightness level, LCDs consume less energy than OLEDs. This is a problem we have to face. For mobile devices, higher brightness means better visibility outdoors, while products like TV only need to have enough brightness during the day.
On the other hand, the power consumption of an OLED panel depends on how many pixels are there, so a higher resolution OLED screen consumes more power.
Cost efficiency: LCD wins
At present, LCD is the lowest cost display, but OLED technology is constantly being optimized with continuous progress and time. At present, the specific cost rate is still unclear, but in the future, OLED technology will continue to improve, and eventually it will continue to optimize and reduce the cost, and eventually it will be comparable to LCD.
Summary: OLED is best, but still needs development
In general, OLED has won a great victory in the comparison of image quality parameters, so the future can be said to be a development trend of future display technology. However, OLEDs are still limited by production costs, and the size has also encountered bottlenecks. Unless you have special requirements for specific parameters such as brightness, OLEDs are better than LCDs in most of the display parameters.
However, the cost is also an aspect that has to be considered. The smart phone is okay. If a large-sized display device such as a TV is used, the price of the OLED is almost several times that of the LCD. So how to choose, but also look at your wallet.

About this item
- 9V Switching wall charger
- 110V input voltage / 9VDC 1A/2A/3A... output voltage
- For use with Arduino Uno, Mega and MB102 Power supply boards
- Connector size: 5.5 x 2.1mm/5.5*2.5mm...
- Center or Tip is positive, sleeve is negative
9v wall charger,AC Power Supply Wall Plug,Wall Adapter Power Supply,9V Power Adapter,ac 50/60hz power adapter,Wall Adapter Power Supply - 9VDC,100-240v converter switching power adapter
Shenzhen Waweis Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.szwaweischarger.com